There is no human survival without water. We need clean water for drinking, cooking, and ensuring cleanliness. Interestingly, the water requirement of an average person is 20-50 liters every day.
Water can be contaminated – dirty and deadly water with grave consequences on the health. Over 1.8 million deaths are recorded annually from cholera and other diarrheal diseases. The numbers are even higher for victims of severe illnesses associated with preventable water-related diseases.
Sulfur finds its way into the water in various ways. So, how harmful is this chemical element in the body? Let’s see the answers together.
Is Sulfur odorless? If not, what is its smell?
Sulfur is not odorless. It releases the typical sulfur smell when sulfur bacteria break down the organic matter. The gas released is the hydrogen sulfide gas, which characteristically smells like a rotten egg. You will find Sulfur in groundwater, so we can attribute its harmless smell to several reactions occurring in your hot water.
Water may smell oddly sometimes, especially if you get it from a well or similar still supplies. If the sulfur smell is strong – just like rotten eggs – you may have sulfur bacteria or hydrogen sulfide somewhere in the mix. Although there are no immediate dangers, in that case, the smell may indicate high pollution levels or chemical presence. Scientists have found over 316 contaminants in water reservoirs across the country. The only way to make water safe and clean is to identify where this odor comes from.
How did Sulfur get into the water?
If your water gives off a sulfur smell only when it is hot, then you may have the sulfate-reducing bacteria in your water tank. The sulfate to hydrogen sulfide gas conversion happens more often in a water heater. The heater produces hydrogen sulfide gas either by creating a warm environment for the thriving of the bacteria or facilitating the reaction between the sulfate in the water and the water heater’s anode. The anode, which is a ¾ inches wide and 30-40 inches long metal rod installed in the heater to reduce the water heater tank corrosion, is made of magnesium metal. The metal can be a source of electrons to facilitate the sulfate to hydrogen sulfide gas conversion.
If both your hot and cold water gives off a sulfur smell, then your water source most likely has hydrogen sulfide gas in it. Underground water contaminated with hydrogen sulfide gas is the most difficult and most expensive to fix. It requires several water tests and extensive water treatment systems.
How safe is water with a sulfur smell for drinking?
Your water may not be unsafe for drinking despite the Sulfur or chlorine smell. That said, a change in the taste, smell, or appearance of your water may impair your water drinking experience. Therefore, carry out tests to identify the source and other potentially harmful components of your water. That way, you can come up with the right treatment options.
How do you get rid of the sulfur smell in water?
Reverse Osmosis
The reverse osmosis water systems rely on the reverse osmosis effect to purify water. The raw water side of the RO reverse osmosis membrane is subjected to a specific voltage, creating a pressure difference on either side of the membrane. With this pressure difference, the high-concentration molecules on one side of the membrane are forced through the reverse osmosis membrane, completing filtration and purification. As a result, the RO membrane allows the passage of only water molecules while keeping out heavy metals and other contaminants.
You can remove almost all impurities in your water with the RO reverse osmosis filter, with a 99.99% theoretical filtration rate. The effluent in the RO reverse osmosis water purification process is the pure, drinking water.
Waterdrop D6 600GPD Reverse Osmosis Water Filter System
The 5-in-1 composite reverse osmosis filter in the Waterdrop D6 RO water filter system, combined with a DOW reverse osmosis membrane with a pore size of 0.0001 micrometers, gives the best filtration results you can expect of any RO water filter. It is effective against multiple water pollutants, including nitrates, benzene, chromium, sodium lead, PFAs, chlorine, lead, and even TDS.
Here are the five layers and what they do;
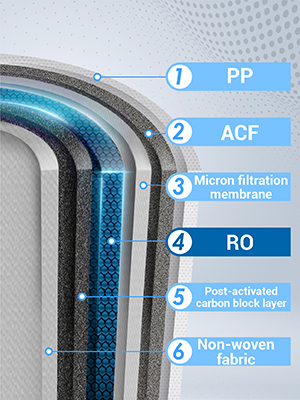
| Layers | Function |
| First PP cotton layer | Filters out sediment, rust, and other large particles |
| Activated carbon fiber layer | Reduces organic matter and chlorine |
| Second PP cotton layer | Further reduces suspended matter and other impurities |
| reverse osmosis membrane layer | Has a filtration accuracy of 0.0001 μm, which intercepts TDS, salt, nitrates, PFAS, lead, sodium, chromium, benzene, etc. |
| Post-activated carbon block layer | Reduces taste and odor to improve the taste of water |
G3P800 Tankless 800GPD RO System
While the traditional RO systems also remove the beneficial minerals during filtration, the Waterdrop G3P800 does not. Instead, thanks to its inbuilt remineralized water filter, it produces filtered but mineralized water. Now you can be sure of getting all the beneficial minerals you need in your drinking water. Here is an article about why you should choose a tankless reverse osmosis system.
In Conclusion
You need water in your body to move nutrients to and from cells, expel metabolic wastes, and facilitate nutrient exchange among capillaries, tissue fluids, and cells. All these collectively ensure stable cellular homeostasis. There is more to learn about drinking water; find out here.




